What am I looking at?
Lymph nodes are solitary ovoid structures composed of lymphoid tissue and are distributed along the lymphatic vessels.
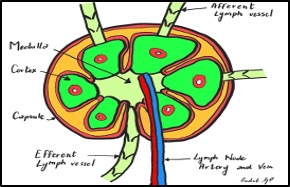
Figure 2. Lymph node- illustration. Image Source: Dr. Giulia Pula 2024.
Each node is divided internally into cortex and medulla and encased by a capsule. Artery and vein enter and exit the lymph node at the hilum.
On ultrasound, the skin and subcutaneous tissue are the most superficial layers, with muscle groups just beneath. Depending on the location of the lymph node, you may also see surrounding structures such as the carotid artery, internal jugular vein, trachea, or adjacent glands (e.g., thyroid, submandibular). The lymph nodes themselves are visualized within the soft tissue between these landmarks. Vessels will appear as anechoic structures, tubular and elongated in the long axis or round and circular in the short axis, while glands demonstrate a more homogeneous, finely echogenic texture compared to surrounding muscle.
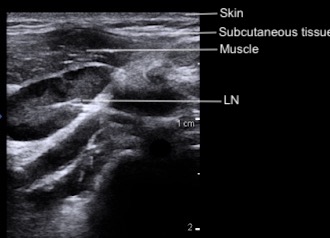
Figure 3: Cervical layers and normal lymph node on POCUS
