Indications
- All trauma patients in whom a chest x-ray is indicated or a FAST exam is performed
- Clinical suspicion of pleural effusion
- During systematic assessment of lungs with PoCUS in dyspneic patient
Equipment
- Ultrasound machine
- Curvilinear or phased array probe
- Gel
Technique
1) Select the appropriate probe for the patient size
2) Position the patient: sitting preferred over supine
> In the seated patient: Place the probe longitudinally in the posterior mid-scapular line at the level of the xiphoid.
> In the supine or reclined patient: Place the probe longitudinally in the posterior axillary line at the level of the xiphoid and fan as posteriorly as possible to identify any dependent fluid.
3) Center the diaphragm in the screen
4) Identify the diaphragm, liver (or spleen on the left), pleura and lung
5) Look for normal artifacts and abnormal findings and store/save images and clips to document your findings.
6) If an effusion is identified, assess in the transverse plane
i) Rotate the probe 90 degrees clockwise into a transverse position (probe marker posterior on the right side and anterior on the left side)
ii) Move probe to the axilla, slide the probe down across each intercostal space until the diaphragm is visualized – store a clip capturing this axilla-diaphragm assessment.
iii) At the level of the largest fluid pocket, fan the probe cephalad and caudad within that intercostal space to fully assess the extent of the effusion – Store a second clip of this focused sweep.
7) Repeat the above steps on opposite side
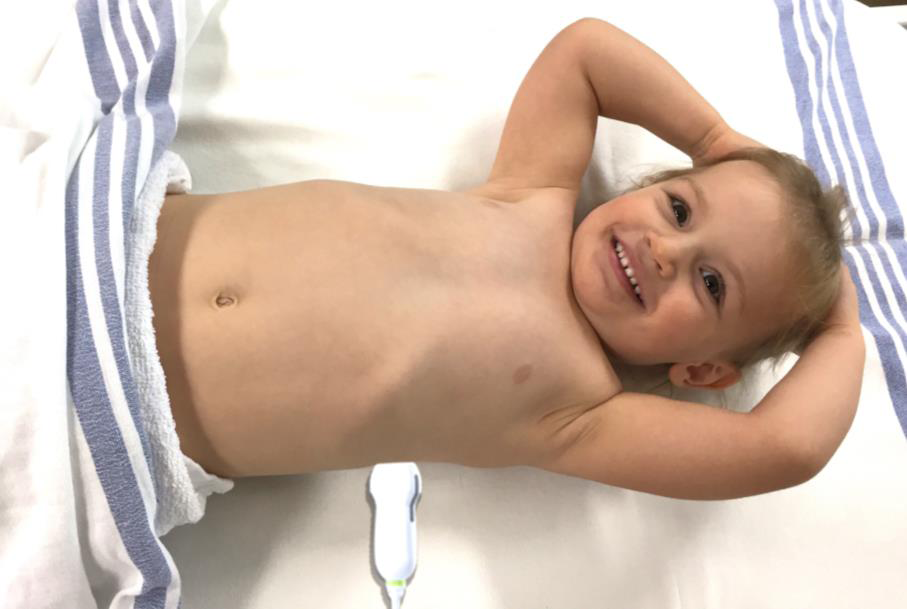 Figure 2: Sagittal Assessment Probe Position
Figure 2: Sagittal Assessment Probe Position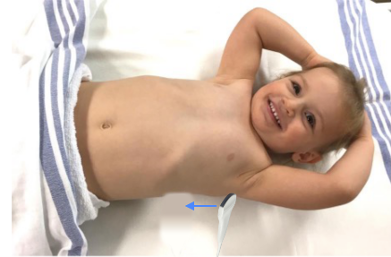
TIPS
- Consider patient size when selecting a probe
- Lift the ipsilateral arm to open rib spaces
- In the supine patient ensure you place and angle the US as posterior as possible to visualize dependent fluid
- If having trouble visualizing the diaphragm first move the probe cephalad/caudal followed by anterior/posterior on the chest to optimize the image
- A posterior approach with the probe in the mid-scapular line can also be used: the landmarks remain the same with the exception of the vertebrae which are not visualized—this approach can be useful in fearful children who prefer to remain seated in their parents lap and hug their parents exposing their back to the examiner
